High-Dimensional Simulation Optimization via Brownian Fields and Sparse Grids
Jul 19, 2021· ,
, ·
0 min read
·
0 min read
Liang Ding
Rui Tuo
Xiaowei Zhang
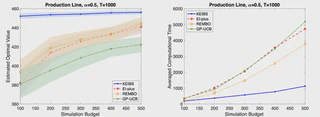
Abstract
High-dimensional simulation optimization is notoriously challenging. We propose a new sampling algorithm that converges to a global optimal solution and suffers minimally from the curse of dimensionality. The algorithm consists of two stages. First, we take samples following a sparse grid experimental design and approximate the response surface via kernel ridge regression with a Brownian field kernel. Second, we follow the expected improvement strategy—with critical modifications that boost the algorithm’s sample efficiency—to iteratively sample from the next level of the sparse grid. Under mild conditions on the smoothness of the response surface and the simulation noise, we establish upper bounds on the convergence rate for both noise-free and noisy simulation samples. These upper bounds deteriorate only slightly in the dimension of the feasible set, and they can be improved if the objective function is known to be of a higher-order smoothness. Extensive numerical experiments demonstrate that the proposed algorithm dramatically outperforms typical alternatives in practice.
Type
Simulation Optimization
Kernel Ridge Regression
Expected Improvement
Brownian Field
Sparse Grid
Gaussian Process
Tensor Markov Kernel
Experimental Design
Matrix Inversion
High-Dimensional
Convergence Rate

Authors

Authors
I am an Associate Professor at HKUST, jointly appointed in the Department of Industrial Engineering and Decision Analytics and the Department of Economics, and the Academic Director of the MSc in FinTech program. I serve as an Associate Editor for several leading journals in the field, including Management Science, Operations Research, Navel Research Logistics, and Queueing Systems.