Learning to Simulate: Generative Metamodeling via Quantile Regression
Jan 20, 2026·


 ·
0 min read
·
0 min read
L. Jeff Hong
Yanxi Hou
Qingkai Zhang
Xiaowei Zhang
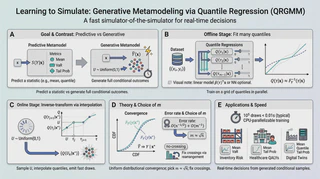
Abstract
Stochastic simulation models effectively capture complex system dynamics but are often too slow for real-time decision-making. Traditional metamodeling techniques learn relationships between simulator inputs and a single output summary statistic, such as the mean or median. These techniques enable real-time predictions without additional simulations. However, they require prior selection of one appropriate output summary statistic, limiting their flexibility in practical applications. We propose a new concept: generative metamodeling. It aims to construct a ‘‘fast simulator of the simulator,’’ generating random outputs significantly faster than the original simulator while preserving approximately equal conditional distributions. Generative metamodels enable rapid generation of numerous random outputs upon input specification, facilitating immediate computation of any summary statistic for real-time decision-making. We introduce a new algorithm, quantile-regression-based generative metamodeling (QRGMM), and establish its distributional convergence and convergence rate. Extensive numerical experiments demonstrate QRGMM’s efficacy compared to other state-of-the-art generative algorithms in practical real-time decision-making scenarios.
Type
Publication
INFORMS Journal on Computing, 2nd Round Review

Authors
Professor in Department of Industrial and Systems Engineering at the University of Minnesota.


Authors
Ph.D. student in Management Science at City Univeristy of Hong Kong and Fudan University.

Authors
I am an Associate Professor at HKUST, jointly appointed in the Department of Industrial Engineering and Decision Analytics and the Department of Economics, and the Academic Director of the MSc in FinTech program. I serve as an Associate Editor for several leading journals in the field, including Management Science, Operations Research, Navel Research Logistics, and Queueing Systems.